Understand the UFE treatment.
UTERINE FIBROID EMBOLIZATION TREATMENT
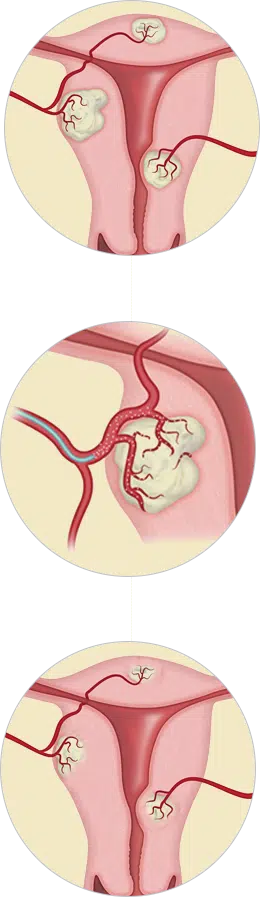
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), also known as uterine artery embolization (UAE), begins with a tiny incision in the groin area or wrist. This incision provides the interventional radiologist (IR) with access to arteries that feed the fibroids. Using specialized X-ray equipment, the IR passes a catheter (small tube) into the incision to the uterine artery, and guides it near the location of the fibroid tumor.
When the IR has reached the location of the fibroids, embolic material (small spheres) is injected through the catheter and into the blood vessels feeding the fibroids, depriving them of oxygenated blood. The oxygen deprivation results in the fibroids shrinking. The embolic material remains permanently in the blood vessels at the fibroid site. The catheter is then moved to the other side of the uterus. Once the IR has completed embolization of the uterine artery on both sides, the catheter is gently removed.
The entire UFE treatment typically lasts less than one hour and is typically performed as an outpatient procedure.